
Researchers from Ben-Gurion University, studying hidden methods of data transmission from isolated computers, have developed a new method organization of a communication channel called «AIR-FI», which allows, through manipulating DDR memory chips, generate a radio signal at a frequency of 2.4 GHz, which can be captured by a device enabled for Wi-Fi several meters away.
From a practical point of view, the method can be used to transfer encryption keys, passwords, and secret data from a computer that has no network connection and is infected with spyware or malware.
About AIR-FI
Los investigadores managed to achieve a transfer rate of 100 bits per second placing receivers Wi-Fi, such as a smartphone or laptop, at a distance of 180 cm. The transmission error rate was 8,75%, but error correcting codes were used to identify and correct transmission faults.
To organize a data transfer channel, just start a normal user process, who it can be run in a virtual machine. For reception, a device with a wireless chip capable of low-level air monitoring is required (in the experiment, wireless adapters based on Atheros AR92xx and AR93xx chips were used with modified firmware that transmit information about the signal parameters suitable for spectral analysis).
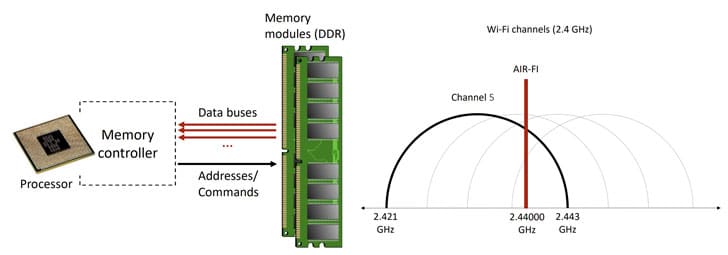
When generating a signal, DDR4-2400 memory capacity was used operating at a frequency of 2400 MHz to generate electromagnetic interference when the controller accesses the memory module through different data buses.
The Wi-Fi range falls in the frequencies 2.400-2.490 GHz, that is, it crosses the frequency at which the memory operates.
Los investigadores have found that with heavy traffic simultaneous on different data buses, electromagnetic waves are emitted at a frequency of 2,44 Ghz, which are captured by the 802.11 wireless stack.
With memory modules other than DDR4-2400, the method is applicable when the memory frequency is programmatically changed, which is allowed in the XMP (Extreme Memory Profile) specification.
To generate a signal, simultaneous access to the bus was used from parallel execution threads tied to different CPU cores. Information encoding useful in signal is carried out using OOK modulation simpler (on-off encoding) with amplitude shift keying (ASK), in which "0" and "1" are encoded by setting different signal amplitudes, and information is transmitted at a fixed rate. - one bit per millisecond.
Transfer "1" performs a series of memory writes caused by the sequential copying of 1 MB of data between the two arrays. When transmitting "0", the algorithm takes no action during the time allotted to transmit a bit. Therefore, the transmission of "1" generates the signal emission, and the transmission of "0" the signal disappears.
Among the measures to counteract the use of the AIR-FI method, the zoning of the territory is mentioned with the creation of a perimeter in the organizationn, within which it is prohibited to carry equipment with wireless chips, as well as placing the computer case in a Faraday cage, generating noise on Wi-Fi frequencies, starting background processes that are randomly performed memory operations and monitoring the appearance in the system of suspicious processes that perform abnormal memory operations.
In addition, on the researchers page, a selection of transmission methods is formed of hidden data they identified using electromagnetic, acoustic, thermal and light leakage forms:
- PowerHammer: Organize the sending of data over the power line, manipulate the load on the CPU to change the power consumption. ODINI: Demonstrations of data extraction from a device located in a shielded room (Faraday cage) by analysis low frequency magnetic oscillations that occur during CPU operation.
- MAGNETO: data extraction based on the measurement of magnetic field fluctuations that occur during CPU operation.
- AirHopper: data transfer at a rate of up to 60 bytes per second from a PC to a smartphone through analysis on a smartphone with an FM tuner of radio interference that occurs when information is displayed on the screen.
- BitWhisper - Data transfer over a distance of up to 40cm at a rate of 1-8 bits per hour by measuring fluctuations in the temperature of the PC case.
- GSMem: extraction of data at a distance of up to 30 meters by creating electromagnetic interference on the frequency of GSM networks captured by the smartphone.
Source: https://cyber.bgu.ac.il