Chandelier It is an Open Source distributed file system, normally used in large-scale clusters. The name is a mix of Linux and clusters.
The project attempts to provide a file system for clusters of tens of thousands of nodes with petabytes of storage capacity, without compromising speed or security, and is available under the GNU GPL.
Cluster File Systems are the designers, developers and maintainers of Luster with contributions from other companies and individuals.
About Luster
Many of the fastest supercomputers in the world are clusters that use the Luster file system for storage, like systems in ORNL, PNNL, LLNL, and LANL.
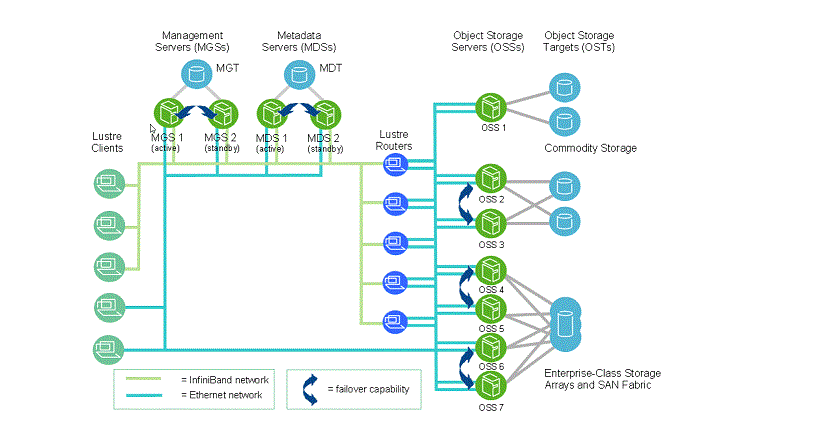
This system considers each file stored in the Luster file system an object. Luster introduces all clients to standard POSIX semantics and concurrent read and write access for shared objects. A Luster file system has four functional units.
These are Meta data server (MDS) to store the metadata; an Object storage target (OST) to save the actual data; an Object storage server (OSS) to manage the OSTs; customer (s) to access and use the data.
OSTs are block devices. An MDS, OSS, and an OST can reside on the same node or on different nodes.
Luster does not directly manage the OSTs, and delegates this responsibility to the OSSs to ensure scalability for large clusters and supercomputers.
In a Massively Parallell Processor (MPP), processors can access the Luster file system by redirecting their I / O requests to the node with the task launcher service if it is configured as a Luster client.
Although it is the simplest method, it generally provides poor performance. A slightly more complicated way to provide very good overall performance is to use the libluster library.
Libluster is a user-level library that enables processors to mount and use the Luster file system as a client, bypassing redirection to the service node.
Using libluster, processors can access the Luster file system, even if the service node on which the job was launched is not a Luster client.
Libluster provides a mechanism to move data directly between the application space and the Luster OSSs without the need to make a data copy through the lightweight core, thus achieving low latency, and high bandwidth in the direct access of the processors to the Luster file system.
New version of Luster
Recientemente a new version of Luster 2.12 was released with which some new functions and above all bug fixes have been added for some of the various Linux distributions that are used for supercomputers.
Main novelties of Luster 2.12
With this new release added the function of spacing existing large directories of distributed namespace (DNE, Distributed Namespace) from one metadata storage object (DTM, metadata targets) to many (spacing different DNE segments by different DTMs).
The new feature simplifies the introduction of new MDTs for existing FSs and manual rebalancing of the load in MDT.
For metadata repositories (MDT), the »Lazy Size« mode is implemented, which allows you to quickly return the approximate size rather than the exact size of the files when directly scanning MDT through the policy engine in situations where the speed is more important than precision.
For configurations with multiple LNet network interfaces, in this new version of Luster 2.12 the «LNet Network Health» function is added, which implements the option to re-access RPC through another network interface in case of failure the first time a request is sent.
In addition to this, server support was added for versions of RHEL 7.6 (3.10.0-957.el7) and SLES12 SP3 (4.4.162-94.69). Added customer support for unpatched RHEL 7.6 (3.10.0-957.el7), SLES12 SP3 (4.4.162-94.69) and Ubuntu 18.04 (4.15.0-32) kernels.