We all know that it exists fragmentation in main and secondary memory. This fragmentation is almost negligible on certain file systems, but very evident on others. In Linux, and the UNIX world in general, fragmentation is not a big problem. Fragmentation is generally quite low. By the way, in case you don't know, fragmentation is when a file or data is not stored consecutively in memory, but instead is stored in several separate areas ...
This is done to help the operating system to use the available memory space on a device or medium, if it does not exist, blocks should be continuously moved to re-house the new written data and constantly update to have them located, without being able to write quickly. But that in the long run slows down access (read and write) of these blocks and that causes memory resources to end up being used inefficiently.
Many are aware of hard drive fragmentation, but are unaware that RAM memory fragmentation also exists in the same way it exists on secondary storage media. But another thing they don't know is that There are two types fragmentation:
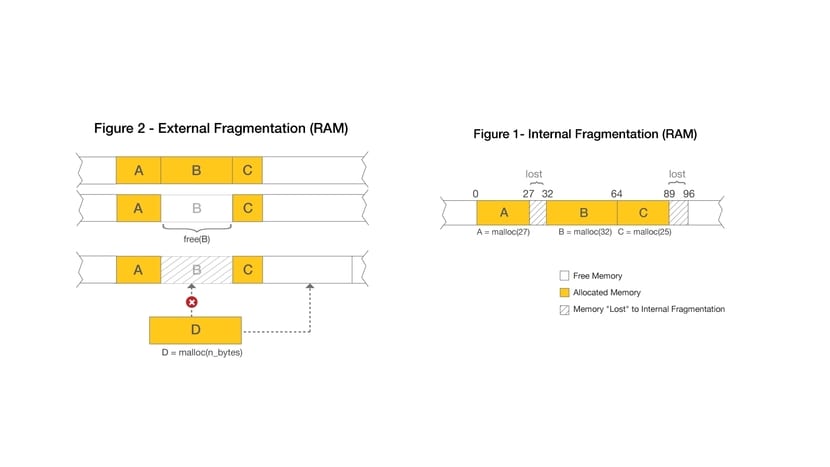
- Internal fragmentation- It is a type where the system memory is over-provisioned and then cannot be used. For example, if you look at the image of the article, you see that to house block A it was estimated that it would occupy something more and now that excess space (grated) cannot be used.
- External fragmentation- Occurs when an application or process or data is removed from memory and used space is not immediately reallocated, leaving a chunk.
- Data fragmentation: when data is written non-sequentially.
- Bubbles: it is the fragmentation in this case of the free space, when it is not uniform and compact, but is divided into small free pieces intertwined with other occupied blocks. That makes writing more complicated.
You already know which file systems or FS like ext4, ZFS, Reiser4, etc., they do not usually have a capital fragmentation and generally do not need to defragment frequently ...