The FBI and NSA released a security alert yesterday collectively containing details of a new malware affecting Linux and that according to the two agencies, It was developed and deployed in real attacks by Russian military hackers.
Both agencies claim that Russian hackers used the malware, called drovorub, to install backdoors inside hacked networks.
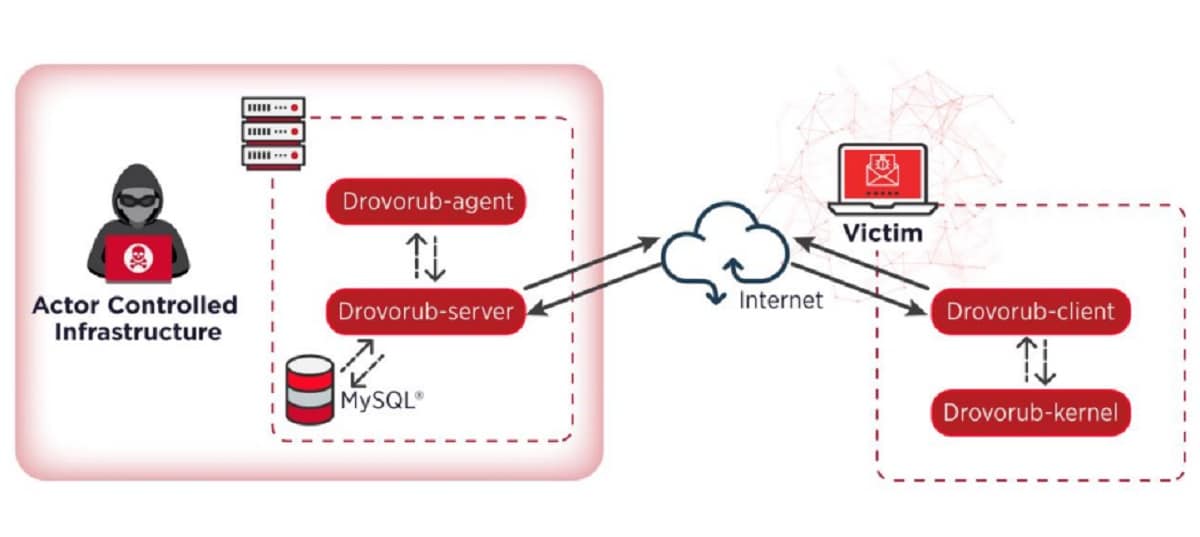
About Drovorub
Malware has different modules that guarantee stealth, persistence and full access to the machine committed to the highest privileges.
In the technical report released by the NSA and the FBI, Details on Drovorub's Capabilities and Proposals for Detection Solutions Released and prevention.
According to the report, the rootkit is very effective in hiding on an infected machine and survives reboots unless:
"Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) Secure Boot is enabled in" Full "or" Full "mode.
The report describes the technical details of each part of Drovorub, that communicate with each other via JSON over WebSockets and encrypt the traffic to and from the server module using the RSA algorithm.
NSA and the FBI attributed the malware to the main Intelligence Directorate of the Russian General Staff, 85th. Main Special Services Center (GTsSS), Military Unit 26165.
The cyber activity of this organization is linked to the campaigns of the advanced hacking collective known as Fancy Bear (APT28, Strontium, Group 74, PawnStorm, Sednit, Sofacy, Iron Twilight).
This allocation is based on the operational command and control infrastructure that companies have publicly associated with the GTsSS to defend against cyberattacks. One clue is an IP address that Microsoft found in a Strontium campaign operating IoT devices in April 2019 and also used to access Drovorub C2 during the same period.
Detection and prevention
The NSA investigation has determined that malware activity is visible through additional detection techniques, but these are not very effective for the Drovorub kernel module.
Network intrusion detection systems (NIDS) like Meerkat, Snort, Zeek can dynamically unlock messages WebSocket protocol "hidden" (using scripts) and identify C2 messages between the client and agent components and the Drovorub server.
A TLS proxy would achieve the same result even if the communication channel uses TLS for encryption. However, one caveat with these methods is that peering can go unnoticed if TLS is used or if the actor switches to a different message format.
For discovery host-based, the NSA and the FBI offer the following solutions:
- Test the presence of the Drovorub kernel module using a script included in the report (on page 35)
- Security products that can detect malware artifacts and rootkit functionality, such as the Linux kernel auditing system;
- Live response techniques, searching for specific filenames, paths, hashes, and with Yara's rules (provided in Snort's rules report)
- Memory scan, the most efficient way to find the rootkit;
- Disk image scanning, malware artifacts are persistent on disk, but rootkits hide them from binary files and normal system calls.
As prevention methods, both agencies recommend installing the latest Linux updates and use the latest available software versions.
In addition, system administrators they should make sure the machines are running at least Linux kernel 3.7, which offers the implementation of the kernel signature. Configuring systems to only load modules that have a valid digital signature increases the level of difficulty in blocking malicious kernel modules.
Another recommendation is to enable the UEFI Secure Boot verification mechanism (full application) that only allows legitimate kernel modules to be loaded. However, this does not protect against the recently disclosed BootHole vulnerability.
Source: https://www.zdnet.com